


ALPHOID DNA VARIATIONS AND NON-DISJUNCTION
IN DOWN’S SYNDROME: FLUORESCENCE IN SITU
HYBRIDIZATION AND CYTOGENETIC STUDIES
Vorsanova SG1,*, Yurov YB2, Beresheva AK1, Iourov IY2,
Monakhov VV2, Sharonin VO1, Demidova IA2, Kravets VS1
*Corresponding Author: Professor Svetlana G. Vorsanova, DSc., Director, Molecular-Cytogenetic Laboratory of Neuropsychiatric Diseases, Institute of Pediatrics and Children Surgery, Russian Ministry of Health, Taldom¬skaya str 2, 127 412 Moscow, Russia; Tel.: +7-095-484-19-48; Fax: +7-095-952-89-40; E-mail: y_yurov@yahoo. com
page: 81
|
|
MATERIALS AND METHODS
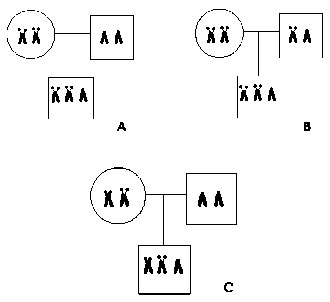
Chromosomal preparations of 36 DS children and their parents were obtained from blood lymphocyte cell lines. Metaphase chromosomes were prepared using standard techniques of colcemid treatment, hypotonic treatment and methanol/acetic acid fixation (3:1) three times for 15 min. before being placed onto slides. Standard karyotyping and detection of chromosomal aberrations with classical GTG-banding were performed. Cytogenetic chromosome analysis was performed on peripheral blood lymphocytes, using the technique described before [6] The morphological pecularities of chromosome 21 were studied (cytologic markers: specificity or presence of satellites, short arm (p) form, etc.) in order to determine the parental origin of chromosome 21 (Fig. 1). Centromeric alphoid chromosome 21-specific DNA probe (aRI-6) corresponding to alphoid array subsets a-21-1 from the collection at the Cytogenetic Laboratory, National Center of Mental Health, Moscow, Russia, was used for FISH [9-11].
In situ hybridizaton was performed as described in detail previously [9,11] using a biotinilated DNA probe. Slides with fixed cells were treated for 2 min. with 70% formamide, 2X SSC at 72°C for chromosomal DNA denaturation, dehydrated in 70, 80, 100% ethanol solutions for 2 min. each and air-dried. DNA probes with a concentration of 20 ng in 10 mL of hybridization solution were denaturated at 100°C for 5 min., placed on ice and then applied to the slides. Fluorescence in situ hybridizations, at high stringency conditions, were performed at 42°C overnight, followed by washing of the slides in 50% formamide, 2X SSC for 15 min. at 42°C. Detection of the biotin-labeled probe was performed by the use of one layer of fluorescein-avidin (Sigma, Moscow, Russia) according to the method of Pinkel et al. [12]. Slides were mounted in antifade solution [0.2% p-phenilenediamine (Sigma) in 80% glycerol, 20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0], and 400 ng/mL propidium iodide and 200 ng/mL DAPI (4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole 2HCl) as counter-staining. Identification of chromosomes was performed by Q-banding, produced by DAPI.
Figure 1. Detection of chromosome 21 origin by cytogenetic analysis. A) Case of maternal meiosis I or II non-disjunction (family #20). B) Uninformative case (family #1). C) Case of maternal meiosis I non-disjunction (family #10)
|
|
|
|



 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (2), 2024 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (1), 2024 |
Number 26
Number 26 VOL. 26(2), 2023 All in one |
Number 26
VOL. 26(2), 2023 |
Number 26
VOL. 26, 2023 Supplement |
Number 26
VOL. 26(1), 2023 |
Number 25
VOL. 25(2), 2022 |
Number 25
VOL. 25 (1), 2022 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(2), 2021 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(1), 2021 |
Number 23
VOL. 23(2), 2020 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(2), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(1), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22, 2019 Supplement |
Number 21
VOL. 21(2), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21 (1), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21, 2018 Supplement |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (2), 2017 |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (1), 2017 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (2), 2016 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (1), 2016 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (2), 2015 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (1), 2015 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (2), 2014 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (1), 2014 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (2), 2013 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (1), 2013 |
Number 15
VOL. 15 (2), 2012 |
Number 15
VOL. 15, 2012 Supplement |
Number 15
Vol. 15 (1), 2012 |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (2), 2011 |
Number 14
The 9th Balkan Congress of Medical Genetics |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (1), 2011 |
Number 13
Vol. 13 (2), 2010 |
Number 13
Vol.13 (1), 2010 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (2), 2009 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (1), 2009 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (2),2008 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (1),2008 |
Number 10
Vol.10 (2), 2007 |
Number 10
10 (1),2007 |
Number 9
1&2, 2006 |
Number 9
3&4, 2006 |
Number 8
1&2, 2005 |
Number 8
3&4, 2004 |
Number 7
1&2, 2004 |
Number 6
3&4, 2003 |
Number 6
1&2, 2003 |
Number 5
3&4, 2002 |
Number 5
1&2, 2002 |
Number 4
Vol.3 (4), 2000 |
Number 4
Vol.2 (4), 1999 |
Number 4
Vol.1 (4), 1998 |
Number 4
3&4, 2001 |
Number 4
1&2, 2001 |
Number 3
Vol.3 (3), 2000 |
Number 3
Vol.2 (3), 1999 |
Number 3
Vol.1 (3), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.3(2), 2000 |
Number 2
Vol.1 (2), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.2 (2), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.3 (1), 2000 |
Number 1
Vol.2 (1), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.1 (1), 1998 |
|
|

