


EVIDENCE FOR LARGE SCALE CHROMOSOMAL
VARIATIONS IN NEURONAL CELLS OF THE
FETAL HUMAN BRAIN
Yurov YB1,*, Vostrikov VS1, Monakhov VV1, Iourov IY1, Vorsanova SG2,*
*Corresponding Author: Professor Yuri B. Yurov and Professor Svetlana G. Vorsanova, Cytogenetic LaboraČtory; National Center of Mental Health, Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Zagorodnoe shosse 2, Moscow 113 152, Russia; Tel.: +7-095-952-89-90; Fax: 7-095-952-89-40; E-mail: y_yurov@hotmail.com; y_yurov@ yahoo.com
page: 95
|
|
RESULTS
The mFISH studies allowed multicolor detection of numerous targets in interphase nuclei of non dividing neuronal cells, obtained from the fetal brain (Fig. 1). The technique applied in the present study provides accurate identification of individual chromosomes with application of the original collection of DNA probes, and to success in investigating the chromosomal variations in the fetal human brain. Interphase FISH signal scoring was performed using 1,000 nuclei per sample of the fetal brain. The frequencies of aneuploidies involving different chromosomes (numbers of chromosomal aneuploidies per nuclei in percent) were determined. The results are present in Table 1. There is high variability in the frequencies of aneuploidies between samples of fetal brains and different chromosomes in individual brains. The frequencies of chromosomally abnormal nuclei (nullesomy, monosomy, trysomy and tetrasomy) varied from 0.2 to 15.6% for different chromosomes. We have not found any specific aneuploidies characteristic for individual fetal brain samples. The spectrum of aneuploidies was non specific: different nuclei usually have one or very rarely two (or more) chromosomal simultaneous abnormalities. The mean frequencies of aneuploidies determined for 10 samples of fetal brain are 5% for chromosome 1; 3.7% for chromosomes 13 and 21; 1.8% for chromosome 18; 5.8% for chromosome X and 5.7% for chromosome Y. More common aneuploidies were associated with aberrations involving sex chromosomes and chromosome 1. The sum of the frequencies of aneuplodies (or mean cumulative frequency) involving chromosomes 1, 13, 18, 21, X and Y was 22%.
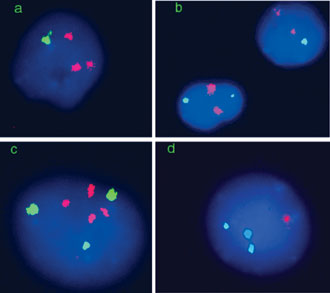
Figure 1. Examples of interphase FISH in fetal human brain. (a) Three red signals with chromosomes 13/21- specific probe (monosomy 13 or 21) and one green signal with chromosome X-specific probe (female); (b) upper: two red signals with chromosome Y-specific probe (disomy Y) and one green signal with chromosome X-specific probe, bottom: two nuclei with one red signal with chromosomes Y-specific probe and one green signal with chromosome X-specific probe; (c) three green signals with chromosome 1-specific probe (trysomy 1) and four red signals with chromosomes 13- and 21-specific probes, (d) three green signals with chromosome 18-specific probe (trisomy 18) and one red signal with chromosome Y-specific probe.
|
|
|
|



 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (2), 2024 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (1), 2024 |
Number 26
Number 26 VOL. 26(2), 2023 All in one |
Number 26
VOL. 26(2), 2023 |
Number 26
VOL. 26, 2023 Supplement |
Number 26
VOL. 26(1), 2023 |
Number 25
VOL. 25(2), 2022 |
Number 25
VOL. 25 (1), 2022 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(2), 2021 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(1), 2021 |
Number 23
VOL. 23(2), 2020 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(2), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(1), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22, 2019 Supplement |
Number 21
VOL. 21(2), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21 (1), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21, 2018 Supplement |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (2), 2017 |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (1), 2017 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (2), 2016 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (1), 2016 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (2), 2015 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (1), 2015 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (2), 2014 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (1), 2014 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (2), 2013 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (1), 2013 |
Number 15
VOL. 15 (2), 2012 |
Number 15
VOL. 15, 2012 Supplement |
Number 15
Vol. 15 (1), 2012 |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (2), 2011 |
Number 14
The 9th Balkan Congress of Medical Genetics |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (1), 2011 |
Number 13
Vol. 13 (2), 2010 |
Number 13
Vol.13 (1), 2010 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (2), 2009 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (1), 2009 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (2),2008 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (1),2008 |
Number 10
Vol.10 (2), 2007 |
Number 10
10 (1),2007 |
Number 9
1&2, 2006 |
Number 9
3&4, 2006 |
Number 8
1&2, 2005 |
Number 8
3&4, 2004 |
Number 7
1&2, 2004 |
Number 6
3&4, 2003 |
Number 6
1&2, 2003 |
Number 5
3&4, 2002 |
Number 5
1&2, 2002 |
Number 4
Vol.3 (4), 2000 |
Number 4
Vol.2 (4), 1999 |
Number 4
Vol.1 (4), 1998 |
Number 4
3&4, 2001 |
Number 4
1&2, 2001 |
Number 3
Vol.3 (3), 2000 |
Number 3
Vol.2 (3), 1999 |
Number 3
Vol.1 (3), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.3(2), 2000 |
Number 2
Vol.1 (2), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.2 (2), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.3 (1), 2000 |
Number 1
Vol.2 (1), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.1 (1), 1998 |
|
|

