


THE PREVALENCE OF Y CHROMOSOME MICRO-
DELETIONS AMONG INFERTILE MALES
FROM THE REPUBLIC OF MACEDONIA
Plaseski T1,2, Dimitrovski C2, Kocevska B2, Efremov GD1, Plaseska-Karanfilska D1*
*Corresponding Author: Dr. Dijana Plaseska-Karanfilska, Macedonian Academy of Sciences and Arts, Research Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, Av. Krste Misirkov 2, POB 428, 1000 Skopje, Republic of Macedonia; Tel.: +389-2-3235-410 Fax: +389-2-3115-434; E-mail: dijana@manu.edu.mk
page: 39
|
|
RESULTS
This was a prospective study; a total of 109 unselected infertile patients with different sperm counts were screened for the presence of Y-chromosome microdeletions. Representative pictures showing the separation of the multiplex A and B PCR fragments on a 1.8 agarose gel electrophoresis are shown in Figure 1. The deletion of the loci was confirmed if the product of expected size was not obtained after two multiplex PCR analysis and three single primer pair PCR experiments.
No deletion was detected in the group of 50 control fertile males (proven fathers). A total of seven Y microdeletions were detected among the 109 infertile males (six AZFc deletions and one AZFb+c deletion). No deletion was detected in the AZFa region. The Y microdeletions were detected in six patients with azoospermia and one with severe oligozoospermia.
The frequency of Y chromosome deletions among infertile males from the Republic of Macedonia is given in Table 1. The overall frequency of Y-chromosome microdeletions was 6.4%; 16.7% in men with azoospermia and 2.8% in men with oligoasthenoteratozoospermia <5x106/ml. Considering the patients with sperm count <5x106/ml, the microdeletion frequency rate was 9.7% (7/72). No deletion was identified among the infertile patients with oligoasthenoteratozoospermia >5x106/ml and normoasthenoteratozoospermia.
Table 1. Frequency of Y chromosome microdeletions among unselected infertile males from the Republic of Macedonia
|
Infertile men |
No. analyzed |
No. with Y deletion |
Frequency % |
|
Azoospermia |
36 |
6 |
16.7 |
|
Oligoasthenoteratozoospermia <5x106/ml |
36 |
1 |
2.8 |
|
Oligoasthenoteratozoospermia >5x106/ml |
14 |
0 |
0 |
|
Normoasthenoteratozoospermia |
23 |
0 |
0 |
|
Total |
109 |
7 |
6.4 |
Table 2. Andrological findings in infertile males with Y chromosome microdeletions
|
Patient
ID |
Left
testis
(cm3) |
Right
testis
(cm3) |
FSH
(mlU/ml) |
LH
(mlU/ml) |
Testo-sterone
(nmol/L) |
Sperm count
(x106/ml) |
Testicular
histology |
Y
Deletion |
|
Z.A. |
/ |
/ |
/ |
/ |
/ |
0 |
/ |
AZFc |
|
A.A. |
20 |
20 |
6.48 |
6.25 |
21.30 |
<0.1 |
HSG |
AZFc |
|
I.V. |
8 |
14 |
24.10 |
3.46 |
17.72 |
0 |
SCOS |
AZFc |
|
S.B. |
15* |
15 |
22.48 |
6.79 |
8.25 |
0 |
SCOS |
AZFc |
|
S.N. |
/ |
/ |
/ |
/ |
/ |
0 |
/ |
AZFc |
|
Z.S. |
/ |
/ |
/ |
/ |
/ |
0 |
/ |
AZFc |
|
G.A. |
/ |
/ |
/ |
/ |
/ |
0 |
/ |
AZFb+c |
Normal values: MTV, 18.25+6.27; FSH, 1.6-12; LH, 0.8-6.0; Testosterone, 5.2-22.9
* varicocele
The andrological findings of the patients with Y-chromosome microdeletions are given in Table 2. The testis volume, hormonal status and histological findings were available from three patients with AZFc deletion. Two of them (patients I.V and S.B.) presented with reduced testicular volumes, increased FSH, normal LH and testosterone values, azoospermia and testicular histology of SCOS. In addition, varicocele of the left testis was detected in patient S.B. Patient A.A. presented with severe oligozoospermia and hypospermatogenesis; his testicular volumes and hormonal values were in the normal range.
The father of only one patient was available for analysis, and he did not carry the deletion. The paternity was confirmed by DNA analysis.
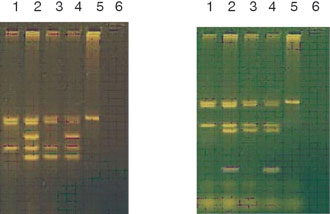
Figure 1. Agarose gel electrophoresis showing the separation of the PCR fragments obtained by Multiplex A and Multiplex B PCR reactions. Line 1, DNA of infertile male with AZFb+c deletion; Line 2, DNA of infertile male without AZF deletions; Lines 3, DNA of infertile male with AZFc deletion; Line 4, control (fertile) male DNA; Line 5, female DNA; Line 6, Blank (no DNA).
|
|
|
|



 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (2), 2024 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (1), 2024 |
Number 26
Number 26 VOL. 26(2), 2023 All in one |
Number 26
VOL. 26(2), 2023 |
Number 26
VOL. 26, 2023 Supplement |
Number 26
VOL. 26(1), 2023 |
Number 25
VOL. 25(2), 2022 |
Number 25
VOL. 25 (1), 2022 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(2), 2021 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(1), 2021 |
Number 23
VOL. 23(2), 2020 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(2), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(1), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22, 2019 Supplement |
Number 21
VOL. 21(2), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21 (1), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21, 2018 Supplement |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (2), 2017 |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (1), 2017 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (2), 2016 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (1), 2016 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (2), 2015 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (1), 2015 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (2), 2014 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (1), 2014 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (2), 2013 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (1), 2013 |
Number 15
VOL. 15 (2), 2012 |
Number 15
VOL. 15, 2012 Supplement |
Number 15
Vol. 15 (1), 2012 |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (2), 2011 |
Number 14
The 9th Balkan Congress of Medical Genetics |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (1), 2011 |
Number 13
Vol. 13 (2), 2010 |
Number 13
Vol.13 (1), 2010 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (2), 2009 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (1), 2009 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (2),2008 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (1),2008 |
Number 10
Vol.10 (2), 2007 |
Number 10
10 (1),2007 |
Number 9
1&2, 2006 |
Number 9
3&4, 2006 |
Number 8
1&2, 2005 |
Number 8
3&4, 2004 |
Number 7
1&2, 2004 |
Number 6
3&4, 2003 |
Number 6
1&2, 2003 |
Number 5
3&4, 2002 |
Number 5
1&2, 2002 |
Number 4
Vol.3 (4), 2000 |
Number 4
Vol.2 (4), 1999 |
Number 4
Vol.1 (4), 1998 |
Number 4
3&4, 2001 |
Number 4
1&2, 2001 |
Number 3
Vol.3 (3), 2000 |
Number 3
Vol.2 (3), 1999 |
Number 3
Vol.1 (3), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.3(2), 2000 |
Number 2
Vol.1 (2), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.2 (2), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.3 (1), 2000 |
Number 1
Vol.2 (1), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.1 (1), 1998 |
|
|

