


CAG REPEAT NUMBER IN ANDROGEN RECEPTOR GENE
AND MALE INFERTILITY
Plaseski T1,2, Noveski P1, Dimitrovski C2, Kocevska B2, Efremov GD1, Plaseska-Karanfilska D1,*
*Corresponding Author: : Dr. Dijana Plaseska-Karanfilska, Macedonian Academy of Sciences and Arts, Research Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, Av. Krste Misirkov 2, POB 428, 1000 Skopje, R. Macedonia; Tel: +389 2 3235 410 Fax: +389 2 3115 434; E-mail: dijana@manu.edu.mk
page: 19
|
|
DISCUSSION
Many studies have investigated the suggested link between increased CAG repeat length in exon 1 of the AR gene and depressed spermatogenesis and male infertility. Studies conducted in China [10], Singapore [11], Japan [12], Australia [13], Greece [14] and France [15], have shown that longer CAG repeats are associated with defective spermatogenesis, while those conducted in Sweden [16], Finland [17], Germany [18], India [19], Italy [20] and Ireland [21], failed to find an association. The ethnic origin of the subjects and patient selection criteria have been suggested as contributing factors for the conflicting reports [20]. To clarify the relevance of CAG repeat size and male infertility, further studies with more homogeneous infertile/subfertile patients should be conducted.
We analyzed the number of CAG repeats among different subgroups of infertile/subfertile patients categorized according to their sperm counts (azoospermia, severe oligozoospermia, mild oligozoospermia and normozoospermia). All those with known causes of spermatogenic failure, such as Y microdeletions, XXY, XX males and obstructive azoospermia were analyzed as a separate subgroup consisting of patients with a known cause of infertility.
This is the first report of the distribution of AR CAG repeats among men from R. Macedonia and the first to correlate the length of AR CAG repeat tracts with the impaired spermatogenesis and male infertility. We failed to find an association between the mean number of CAG repeats among any of the infertile/subfertile subgroups and the fertile controls. However, we found a significantly higher percentage of CAG repeats >26 (p = 0.022), >27 (p = 0.018) and >28 (p = 0.009) in males with mild oligozoospermia. These results indicate a possible association between CAG repeat length and mild oligozoospermia. It is possible that long AR CAG repeat number acts as a low penetrance risk factor, which slightly impairs spermatogenesis, and probably acts in a more complex manner together with other genetic and/or environmental factors. Further studies on a larger number of patients with mild oligozoospermia are warranted to confirm the association between impaired spermatogenesis and mild oligozoospermia
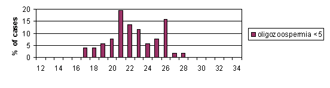
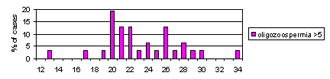
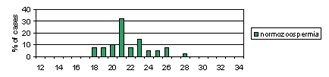
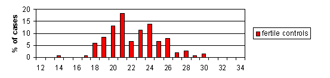
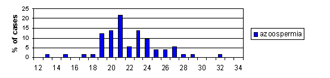
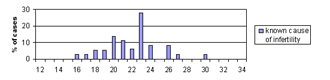
Figure 3. Distribution of CAG repeats in exon 1 of the AR gene in infertile/subfertile males with different sperm counts (azoospermia, n = 73; severe oligozoospermia, n = 51; mild oligozoospermia, n =31; normozoospermia, n = 40), infertile men with known cause of infertility (n = 36 X chromosomes) and in fertile males (n = 152).
Table 1. CAG repeat numbers among different groups of infertile/subfertile patients and fertile controls.
-
|
Group |
Number of
Chromosomes |
CAG Repeat
Range |
Mean + SD |
Median |
|
Azoospermia |
73 |
13–32 |
22.0 + 3.1 |
21.0 |
|
Severe oligozoospermia |
51 |
17–28 |
22.4 + 2.8 |
22.0 |
|
Mild oligozoospermia |
31 |
13–34 |
23.0 +4.2 |
22.0 |
|
Normozoospermia |
40 |
18–28 |
21.8 + 2.4 |
21.0 |
|
Known cause of infertility |
36 |
16–30 |
22.0 + 2.9 |
22.5 |
|
Fertile controls |
152 |
15–30 |
22.3 + 3.9 |
22.0 |
-
Table 2. The percentage of long CAG repeats among different groups of infertile/subfertile patients and fertile controls.
-
|
Group |
CAG Repeats |
|
(number of chromosomes) |
>28 |
>27 |
>26 |
|
|
n (%) |
p Value |
n (%) |
p Value |
n (%) |
p Value |
|
Azoospermia (n = 73) |
2 (2.7) |
0.449 |
3 (4.1) |
0.866 |
7 (9.6) |
0.424 |
|
Severe oligozoospermia (n = 51) |
0 (0.0) |
0.410 |
1 (2.0) |
0.401 |
2 (3.9) |
0.486 |
|
Mild oligozoospermia (n = 31) |
3 (9.7) |
0.009 |
5 (16.1) |
0.018 |
6 (19.4) |
0.022 |
|
Normozoospermia (n = 40) |
0 (0.0) |
0.266 |
1 (2.5) |
0.553 |
1 (2.5) |
0.323 |
|
Known cause of infertility (n = 36) |
1 (2.8) |
0.529 |
1 (2.8) |
0.625 |
2 (5.6) |
0.821 |
|
Fertile controls (n = 152) |
2 (1.3) |
|
7 (4.6) |
|
10 (6.6) |
|
-
-
|
|
|
|



 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (2), 2024 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (1), 2024 |
Number 26
Number 26 VOL. 26(2), 2023 All in one |
Number 26
VOL. 26(2), 2023 |
Number 26
VOL. 26, 2023 Supplement |
Number 26
VOL. 26(1), 2023 |
Number 25
VOL. 25(2), 2022 |
Number 25
VOL. 25 (1), 2022 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(2), 2021 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(1), 2021 |
Number 23
VOL. 23(2), 2020 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(2), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(1), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22, 2019 Supplement |
Number 21
VOL. 21(2), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21 (1), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21, 2018 Supplement |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (2), 2017 |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (1), 2017 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (2), 2016 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (1), 2016 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (2), 2015 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (1), 2015 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (2), 2014 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (1), 2014 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (2), 2013 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (1), 2013 |
Number 15
VOL. 15 (2), 2012 |
Number 15
VOL. 15, 2012 Supplement |
Number 15
Vol. 15 (1), 2012 |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (2), 2011 |
Number 14
The 9th Balkan Congress of Medical Genetics |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (1), 2011 |
Number 13
Vol. 13 (2), 2010 |
Number 13
Vol.13 (1), 2010 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (2), 2009 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (1), 2009 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (2),2008 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (1),2008 |
Number 10
Vol.10 (2), 2007 |
Number 10
10 (1),2007 |
Number 9
1&2, 2006 |
Number 9
3&4, 2006 |
Number 8
1&2, 2005 |
Number 8
3&4, 2004 |
Number 7
1&2, 2004 |
Number 6
3&4, 2003 |
Number 6
1&2, 2003 |
Number 5
3&4, 2002 |
Number 5
1&2, 2002 |
Number 4
Vol.3 (4), 2000 |
Number 4
Vol.2 (4), 1999 |
Number 4
Vol.1 (4), 1998 |
Number 4
3&4, 2001 |
Number 4
1&2, 2001 |
Number 3
Vol.3 (3), 2000 |
Number 3
Vol.2 (3), 1999 |
Number 3
Vol.1 (3), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.3(2), 2000 |
Number 2
Vol.1 (2), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.2 (2), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.3 (1), 2000 |
Number 1
Vol.2 (1), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.1 (1), 1998 |
|
|

