


MOLECULAR ANALYSIS OF HUNTINGTON’S
DISEASE IN THE REPUBLIC OF MACEDONIA
Koceva S1,2, Dimovski AJ1, Plaseska-Karanfiska D1,
Stefanovska A-M1, Vlaski-Jekic S3, Efremov GD1,*
*Corresponding Author: Professor Dr. Georgi D. Efremov, Macedonian Academy of Sciences and Arts, Research Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, Aven Krste Misirkov 2, POB 428, 1000 Skopje, Republic of Macedonia; Tel: +3892-120253; Fax: +3892-115434; E-mail: gde@manu.edu
page: 47
|
|
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients. Ten families from the Republic of Macedonia were included in the analysis of the IT15 gene. Seven patients were referred for diagnostic testing due to the presence of clinical signs consistent with HD, while three individuals required predictive testing due to the presence of the disease in the family. The data on age, gender, family history and type of referral of the patients is summarized in Table 1.
Methods. DNA was isolated from leukocytes using the proteinase K/SDS digestion-phenol/chloroform extraction-ethanol precipitation method, routinely used in our laboratory [9]. The conventional analyses consisted of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis of exon 1 of the IT15 gene, denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) of the resulting fragments, transfer to a nylon membrane, hybridization with a digoxigenin labeled internal probe and visualization by autoradiography [10,11]. Polymerase chain reaction amplification was performed in a reaction volume of 25 mL using 50 ng of genomic DNA, 25 pmol of each primer (direct: 5'-ATG AAG GCC TTC GAG TCC CTC AAG TCC TTC-3' and reverse: 5'-AAA CTC ACG GTC GGT GCA GCG GCT CCT CAG-3'), 10 mM Tris (pH 8.3), 5 mM KCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 200 mM (each) dNTPs, 10% dimethylsulfoxide and 2.5 U of Taq polymerase (AmpliTaq Gold; Applied BioSystems, Palo Alto, CA, USA). After initial heating at 94EC for 10 min, the reaction mix was subjected to 40 cycles of amplification, each consisting of incubation for 1 min at 94EC, 1 min at 60EC and 2 min at 72EC. Two mL of each PCR were diluted with two volumes of 95% formamide loading dye and heat denatured for 2 min at 95EC. The products were resolved on a 6% denaturing polyacrylamide gel (40 x 20 cm x 0.4 mm) containing 6 M urea and 32% formamide. The electrophoresis was run at 70 W constant power for 2 hours and the fragments were transferred to a positively charged nylon membrane (Hybond+; Amersham BioSciences UK Ltd., Little Chalfont, Buckinghamshire, England). The membranes were hybridized with a non radioactively labeled oligonucleotide probe (5’-CAG CAG CAG CAG CAG CG-3’) and detected by chemiluminescence. Details for non radioactive labeling of oligonucleotide probes, allele specific hybridization and chemiluminiscent detection are as given previously [10,11]. A representative autoradioagram showing the results obtained using the PCR-PAGE method is given in Fig. 1. The results obtained with the non radioactive PCR-PAGE method were compared with the results obtained with automated fluorescent PCR/ capillary electrophoresis analysis using the ABI PRISM™ 310 Genetic Analyzer (Applied BioSystems). In this assay, PCR was performed under the same conditions as described above, the only difference being that the direct primer was labeled at the 5’-end with FAM fluorescent dye. Following amplification, 1-2 mL of the PCR reaction were mixed with 25 mL of deionized formamide and 1 mL of ROX-labeled size marker (Applied BioSystems), denatured for 3 min at 95EC and run on the ABI PRISM™ 310 Genetic Analyzer (Applied BioSystems). The results obtained were analyzed using the GeneScan Software II (Applied BioSystems). Electrophoretograms showing the detection of expanded CAG repeats in exon 1 of the HD gene in two HD patients are shown in Fig. 2.
Table 1. Basic data of individuals included in the molecular analysis of Huntington's disease in the Republic of Macedonia
Patient |
Sex-Age |
Family
History |
Referral |
Allele 1 |
Allele 2 |
M.A. |
M-54 |
None |
D |
18 |
43 |
J.N. |
M-48 |
Yes |
D |
19 |
46 |
I.A. |
M-52 |
Yes |
D |
15 |
44 |
X.P. |
F-50 |
None |
D |
17 |
47 |
I.T. |
F-52 |
Yes |
D |
19 |
42 |
R.M. |
F-54 |
Yes |
D |
26 |
42 |
G.D. |
M-12 |
Yes |
D |
17 |
22 |
S.S. |
F-30 |
Yes |
P |
17 |
42 |
J.M. |
F-32 |
Yes |
P |
26 |
16 |
N.M. |
F-39 |
Yes |
P |
17 |
46 |
D: diagnosis; P: predictive testing
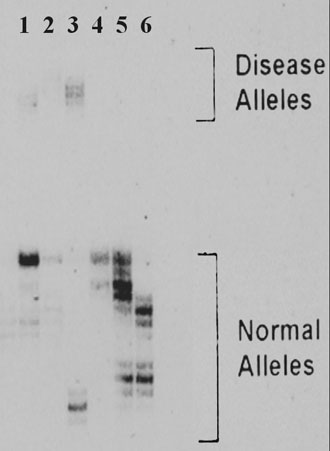
Figure 1. The PCR-PAGE analysis of (CAG)n repeat in exon 1 of the HD gene showing the detection of expanded alleles in three subjects (lanes 1-3).
|
|
|
|



 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (2), 2024 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (1), 2024 |
Number 26
Number 26 VOL. 26(2), 2023 All in one |
Number 26
VOL. 26(2), 2023 |
Number 26
VOL. 26, 2023 Supplement |
Number 26
VOL. 26(1), 2023 |
Number 25
VOL. 25(2), 2022 |
Number 25
VOL. 25 (1), 2022 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(2), 2021 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(1), 2021 |
Number 23
VOL. 23(2), 2020 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(2), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(1), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22, 2019 Supplement |
Number 21
VOL. 21(2), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21 (1), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21, 2018 Supplement |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (2), 2017 |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (1), 2017 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (2), 2016 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (1), 2016 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (2), 2015 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (1), 2015 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (2), 2014 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (1), 2014 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (2), 2013 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (1), 2013 |
Number 15
VOL. 15 (2), 2012 |
Number 15
VOL. 15, 2012 Supplement |
Number 15
Vol. 15 (1), 2012 |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (2), 2011 |
Number 14
The 9th Balkan Congress of Medical Genetics |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (1), 2011 |
Number 13
Vol. 13 (2), 2010 |
Number 13
Vol.13 (1), 2010 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (2), 2009 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (1), 2009 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (2),2008 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (1),2008 |
Number 10
Vol.10 (2), 2007 |
Number 10
10 (1),2007 |
Number 9
1&2, 2006 |
Number 9
3&4, 2006 |
Number 8
1&2, 2005 |
Number 8
3&4, 2004 |
Number 7
1&2, 2004 |
Number 6
3&4, 2003 |
Number 6
1&2, 2003 |
Number 5
3&4, 2002 |
Number 5
1&2, 2002 |
Number 4
Vol.3 (4), 2000 |
Number 4
Vol.2 (4), 1999 |
Number 4
Vol.1 (4), 1998 |
Number 4
3&4, 2001 |
Number 4
1&2, 2001 |
Number 3
Vol.3 (3), 2000 |
Number 3
Vol.2 (3), 1999 |
Number 3
Vol.1 (3), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.3(2), 2000 |
Number 2
Vol.1 (2), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.2 (2), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.3 (1), 2000 |
Number 1
Vol.2 (1), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.1 (1), 1998 |
|
|

