


ANGIOTENSINOGEN POLYMORPHISM M235T
IN PATIENTS WITH ESSENTIAL HYPERTENSION
FROM THE REPUBLIC OF MACEDONIA
Najdanovska N1, Koceva S1,*, Zafirovska K2, Blagoevska M3, Kocova M1
*Corresponding Author: Professor Dr. Mirjana Kocova, Pediatric Clinic, Department of Endocrinology and Genetics, Vodnjanska 17, 1000 Skopje, Republic of Macedonia; Tel.: +389-2-111-713; Fax: +389-2-176-167; E-mail: ozonunit@unet.com.mk
page: 21
|
|
RESULTS
We tested whether there was a significantly different prevalence of angiotensinogen polymorphism M235T between the group of patients with essential hypertension and the control group. We tested separately the prevalence of M235T in the group of patients regarding age and sex, anti-hypertensive therapy and acquired risk factors.
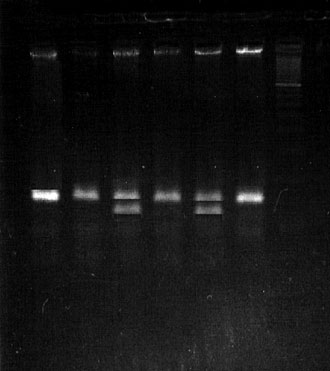
- Undigested PCR product
- homozygote for T235M
- heterozygote for M235T
- homozygore for T235M
- heterozygote for M235T (control)
- homozygote for T235M
- Lader
Figure 1. Restriction fragments separated by electrophoresis on a 2.5% agarose gel.
Description of the Population . Clinical characteristic of the hypertensive patients are given in Table 1. Males prevailed over females (65.0%). The proportion of subjects being administered anti-hypertensive treatment was very high (70.0%). The mean age of onset of essential hypertension was 41.5 ± 9.45. Over 80.0% of the patients had SBP between 120 and 170 mm Hg. Sixty percent of analyzed patients had one or more acquired risk factor(s).
The prevalence of angiotensinogen polymorphism M235T was significantly different between the group of hypertensive patients and controls. We found 55.0% prevalence of angiotensinogen polymorphism M235T in the group of patients with essential hypertension compared to 32.5% prevalence in the control group. The c2 test showed the a statistically significant difference (p <0.04), as shown in Table 2. The mean age of onset of essential hypertension in patients with detected M235T was 41.5 ± 9.45, but we found no statistical significance between the two groups. Seventy-seven percent of patients with essential hypertension who carried M235T were men. Only seven patients (17.5%) had not previously received therapy. However, the c 2 test showed no statistically significant difference. No statistically significant difference has been confirmed for M235T distribution related to acquired risk factor(s).
|
|
|
|



 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (2), 2024 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (1), 2024 |
Number 26
Number 26 VOL. 26(2), 2023 All in one |
Number 26
VOL. 26(2), 2023 |
Number 26
VOL. 26, 2023 Supplement |
Number 26
VOL. 26(1), 2023 |
Number 25
VOL. 25(2), 2022 |
Number 25
VOL. 25 (1), 2022 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(2), 2021 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(1), 2021 |
Number 23
VOL. 23(2), 2020 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(2), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(1), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22, 2019 Supplement |
Number 21
VOL. 21(2), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21 (1), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21, 2018 Supplement |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (2), 2017 |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (1), 2017 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (2), 2016 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (1), 2016 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (2), 2015 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (1), 2015 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (2), 2014 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (1), 2014 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (2), 2013 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (1), 2013 |
Number 15
VOL. 15 (2), 2012 |
Number 15
VOL. 15, 2012 Supplement |
Number 15
Vol. 15 (1), 2012 |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (2), 2011 |
Number 14
The 9th Balkan Congress of Medical Genetics |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (1), 2011 |
Number 13
Vol. 13 (2), 2010 |
Number 13
Vol.13 (1), 2010 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (2), 2009 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (1), 2009 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (2),2008 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (1),2008 |
Number 10
Vol.10 (2), 2007 |
Number 10
10 (1),2007 |
Number 9
1&2, 2006 |
Number 9
3&4, 2006 |
Number 8
1&2, 2005 |
Number 8
3&4, 2004 |
Number 7
1&2, 2004 |
Number 6
3&4, 2003 |
Number 6
1&2, 2003 |
Number 5
3&4, 2002 |
Number 5
1&2, 2002 |
Number 4
Vol.3 (4), 2000 |
Number 4
Vol.2 (4), 1999 |
Number 4
Vol.1 (4), 1998 |
Number 4
3&4, 2001 |
Number 4
1&2, 2001 |
Number 3
Vol.3 (3), 2000 |
Number 3
Vol.2 (3), 1999 |
Number 3
Vol.1 (3), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.3(2), 2000 |
Number 2
Vol.1 (2), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.2 (2), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.3 (1), 2000 |
Number 1
Vol.2 (1), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.1 (1), 1998 |
|
|

