


MLH1 PROMOTER HYPERMETHYLATION IN
BULGARIAN PATIENTS WITH COLORECTAL CANCER
Kadiyska T1,*, Tzancheva M1, Nedin D2, Alexandrova A2,
Marinov M2, Kaneva R1, Damyanov D2, Mitev V3, Kremensky I1
*Corresponding Author: Dr. Tanya Kadiyska, Laboratory of Molecular Pathology, University Hospital of Obstetrics and Gynaecology “Maichin Dom”, 2 Zdrave str., Sofia 1431, Bulgaria; Tel: +359-2-9520124; Fax: +359-2-9520490; E-mail: alextanya@excite.com
page: 3
|
|
RESULTS
The tumors with MLH1 promoter hypermethylation, HpaII failed to cleave the DNA at all four CCGG recognition sites in the region and the PCR reaction gave rise to the expected 603 bp. products (Fig.1). The unmethylated tumors failed to yield PCR products. The PCR reactions after MspI digestion were negative in all the samples. The results of the HpaII digestion and PCR assay were unclear for three MSI-positive tumors. One of them gave in the two assays a weak positive amplification. The other two samples gave weak positive amplification for one reaction and failed to yield a product on a repeat assay using the same template. These results could be due to a partial methylation of the region or methylation in a fraction of DNA molecules. Therefore these tumors were not included in the group of methylated tumors.
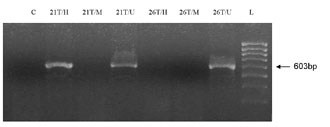
Figure 1 . PCR based HpaII restriction enzyme assay demonstrating (a) a methylated MLH1 promoter region in tumor from MSI(+) patient ?21, and (b) an unmethylated MLH1 promoter region in tumor DNA from MSI(-) patient ?26. (C-negative control, U- undigested; H- incubated with HpaII; M, incubated with MspI; L- DNA Ladder, Low Range (Fermentas))
The MLH1 promoter region was fully methylated in 6 of 25 (24%) of the MSI(+) tumors, but none of the MSI(-) colorectal cancers. There was a significant correlation between hypermethylation of the MLH1 promoter and MSI (p<0.04).
The clinical, pathological, and biomolecular features of the MSI (+) and LOH cases analyzed in relation to their methylation status are reported in Table 1.
In order to interpret the results we examined the patients according to their tumor localization, histological characteristics, degree of instability, age, sex and family history. All MSI(+) methylated tumors were right localized, frequently in I-II stage according the TNM classification, 1 tumor was with poor and 5 were with moderate differentiation. In regard to the mucinous production, there was an accumulation of mucinous type of tumors. Four of the methylated tumors were MSI-H. However these characteristics were shown to be typical for all MSI positive tumors. We found that the correlation between the MLH1 promoter methylation and the MSI(+) sporadic cases was highly significant (p<0.01). In this group there were no patients younger than 50 years (p<0.02).
Full MLH1 promoter methylation was observed also in 5 of 13 (38%) tumors of the LOH patients. These tumors were more frequently with left localization and in I-II stage according the TNM classification. Four of the tumors were with moderate differentiation and less than 50% mucinous production. One tumor was well differentiated and most of the cells were mucin producing. The correlation between MLH1 promoter methylation and the LOH sporadic cases was also significant (p<0.02).
|
|
|
|



 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (2), 2024 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (1), 2024 |
Number 26
Number 26 VOL. 26(2), 2023 All in one |
Number 26
VOL. 26(2), 2023 |
Number 26
VOL. 26, 2023 Supplement |
Number 26
VOL. 26(1), 2023 |
Number 25
VOL. 25(2), 2022 |
Number 25
VOL. 25 (1), 2022 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(2), 2021 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(1), 2021 |
Number 23
VOL. 23(2), 2020 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(2), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(1), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22, 2019 Supplement |
Number 21
VOL. 21(2), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21 (1), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21, 2018 Supplement |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (2), 2017 |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (1), 2017 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (2), 2016 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (1), 2016 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (2), 2015 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (1), 2015 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (2), 2014 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (1), 2014 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (2), 2013 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (1), 2013 |
Number 15
VOL. 15 (2), 2012 |
Number 15
VOL. 15, 2012 Supplement |
Number 15
Vol. 15 (1), 2012 |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (2), 2011 |
Number 14
The 9th Balkan Congress of Medical Genetics |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (1), 2011 |
Number 13
Vol. 13 (2), 2010 |
Number 13
Vol.13 (1), 2010 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (2), 2009 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (1), 2009 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (2),2008 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (1),2008 |
Number 10
Vol.10 (2), 2007 |
Number 10
10 (1),2007 |
Number 9
1&2, 2006 |
Number 9
3&4, 2006 |
Number 8
1&2, 2005 |
Number 8
3&4, 2004 |
Number 7
1&2, 2004 |
Number 6
3&4, 2003 |
Number 6
1&2, 2003 |
Number 5
3&4, 2002 |
Number 5
1&2, 2002 |
Number 4
Vol.3 (4), 2000 |
Number 4
Vol.2 (4), 1999 |
Number 4
Vol.1 (4), 1998 |
Number 4
3&4, 2001 |
Number 4
1&2, 2001 |
Number 3
Vol.3 (3), 2000 |
Number 3
Vol.2 (3), 1999 |
Number 3
Vol.1 (3), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.3(2), 2000 |
Number 2
Vol.1 (2), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.2 (2), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.3 (1), 2000 |
Number 1
Vol.2 (1), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.1 (1), 1998 |
|
|

